A Derby database exists within a system.
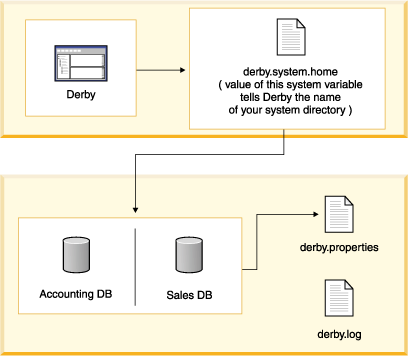
A Derby system is a single instance of the Derby database engine and the environment in which it runs. It consists of a system directory, zero or more databases, and a system-wide configuration. The system directory contains any persistent system-wide configuration parameters, or properties, specific to that system in a properties file called derby.properties. This file is not automatically created; you must create it yourself.
The Derby system is not persistent; you must specify the location of the system directory at every startup.
However, the Derby system and the system directory is an essential part of a running database or databases. Understanding the Derby system is essential to successful development and deployment of Derby applications. As the following figure shows, Derby databases live in a system, which includes system-wide properties, an error log, and one or more databases.
The system directory can also contain an error log file called derby.log (see The error log).
Each database within that system is contained in a subdirectory, which has the same name as the database (see A Derby database).
In addition, if you connect to a database outside the current system, it automatically becomes part of the current system.
When you use the embedded driver, Derby database files and log files normally have whatever default permissions you specify for your file system. If you are running with Java SE 7 or later, however, you can enhance security by restricting file access to the user who creates the database. To do this, set the system property derby.storage.useDefaultFilePermissions to false. See the Derby Reference Manual for details.