Derby can be deployed in a number of ways and in a number of different environments. The security needs of the Derby system are also diverse.
Derby supplies or supports the following optional security mechanisms:
- Authentication
Authentication determines whether you are a legal user. It establishes your identity. Derby verifies user names and passwords before permitting access to the Derby system.
For more information about authentication, see Working with user authentication.
- Authorization
Authorization determines what operations can be performed by you, that is, by your Derby identity. Authorization grants users or roles permission to read a database or to write to a database.
For more information about authorization, see User authorizations.
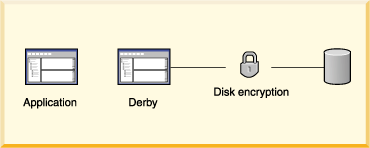
- Disk encryption
Derby provides ways to encrypt data stored on disk.
For more information about encryption, see Encrypting databases on disk.
- Validation of certificates for signed jar files
Derby validates certificates for classes loaded from signed jar files.
For more information about using signed jar files, see Signed jar files.
- Network encryption and authentication
Derby network traffic may be encrypted with SSL/TLS. SSL/TLS certificate authentication is also supported. See "Network encryption and authentication with SSL/TLS" in the Derby Server and Administration Guide for details.
The section "Derby Network Server advanced topics" in the Derby Server and Administration Guide has more information on security issues. The Derby Reference Manual describes many security-related properties and system procedures, as well as such statements as GRANT, REVOKE, CREATE ROLE, DROP ROLE, CREATE PROCEDURE, and CREATE FUNCTION.
Identity in Derby
Derby provides two kinds of identity:
- System-wide identity: Currently, any legal system-wide identity
enjoys authorization to perform the following operations:
- Create databases
- Restore databases
- Shut down the Derby engine
- Database-specific identity: If you are a legal identity in a specific
database, you may enjoy the following rights:
- You can connect to that database, provided that coarse-grained connection authorization has not been set to noAccess.
- You can shut down that database, encrypt it, and upgrade it, provided that you are the database owner.
- You can create your own SQL objects and write data to your own tables, provided that your coarse-grained connection authorization has not been set to readOnlyAccess.
- You can access other SQL objects, provided that the owners have granted you fine-grained SQL access to those objects, and provided you have not been limited by coarse-grained readOnlyAccess.
The distinction between fine-grained SQL authorization and coarse-grained connection organization is described in User authorizations.
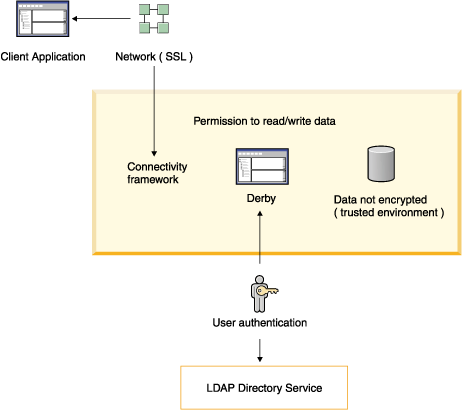
Security mechanisms in action
The following figure shows some of the Derby security mechanisms at work in a client/server environment. User authentication is performed by accessing an LDAP directory service. The data in the database is not encrypted in this trusted environment.
The following figure shows how another Derby security mechanism, disk encryption, protects data when the recipient might not know how to protect data. It is useful for databases deployed in an embedded environment.