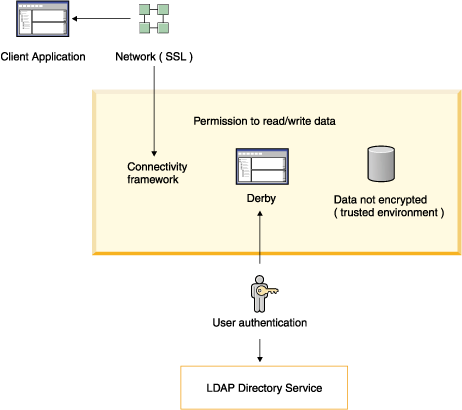
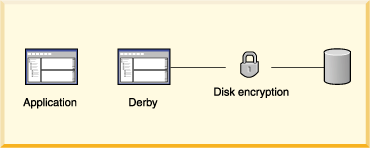
Derby can be deployed in a number of ways and in a number of different environments. The security needs of the Derby system are also diverse.
Derby supplies or supports the following optional security mechanisms:
- User authentication
Derby verifies user names and passwords before permitting them access to the Derby system.
- User authorization
A means of granting specific users permission to read a database or to write to a database.
- Disk encryption
A means of encrypting Derby data stored on disk.
- Validation of Certificate for Signed Jar Files
In a Java 2 environment, Derby validates certificates for classes loaded from signed jar files.
- Network encryption and authentication
Derby network traffic may be encrypted with SSL/TLS. SSL/TLS certificate authentication is also supported. See "Network encryption and authentication with SSL/TLS" in the Derby Server and Administration Guide for details.