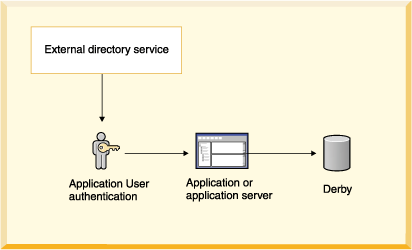
Derby provides support for user authentication. User authentication means that Derby authenticates the name and password for a user before allowing that user access to the system.
When user authentication is enabled (which it is not by default), the user requesting a connection must provide a valid name and password, which Derby verifies against the repository of users defined for the system. After Derby authenticates the user, it grants the user access to the Derby system but not necessarily access to the database made in the connection request. In the Derby system, access to a database is determined by user authorization.
For user authentication, Derby allows you to provide a repository of users in a number of different ways. For example, you can hook Derby up to an external directory service elsewhere in your enterprise, create your own directory service, or use Derby's simple mechanism for creating a built-in repository of users.
You can define a repository of users for a particular database or for an entire system, depending on whether you use system-wide or database-wide properties.
When Derby user authentication is enabled and Derby uses an external directory service, the architecture looks something like that shown in the Figure below:
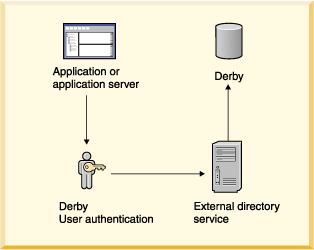
Derby always runs embedded in another Java application, whether that application is a single-user application or a multiple-user application server or connectivity framework. A database can be accessed by only one JVM at a time, so it is possible to deploy a system in which the application in which Derby is embedded, not Derby, handles the user authentication by connecting to an external directory service.